Introducing the Heating Curve Worksheet 2 Answer Key, an invaluable guide that empowers you to decipher the intricate dance of matter as it undergoes thermal transformations. This key unlocks the secrets of heating curves, providing a comprehensive understanding of the stages and calculations involved in this fundamental scientific concept.
Delve into the intricacies of heating curves, unraveling the significance of each stage and the hidden insights they reveal about the behavior of substances. Prepare to master the art of heat capacity calculations, determining the factors that influence a substance’s ability to absorb and release heat.
Heating Curve Basics
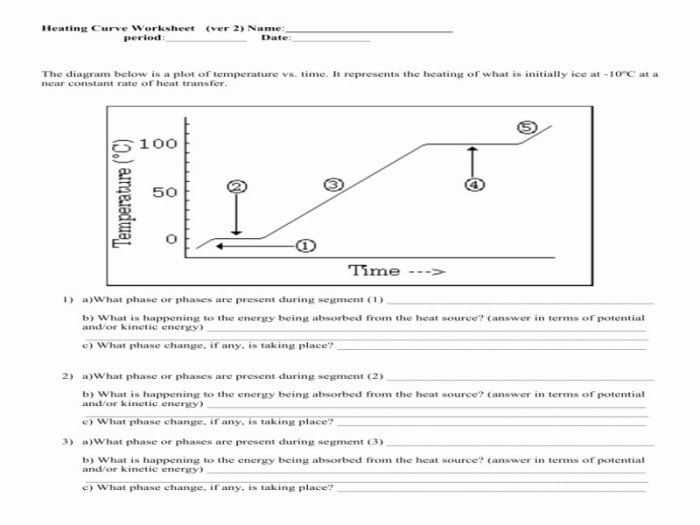
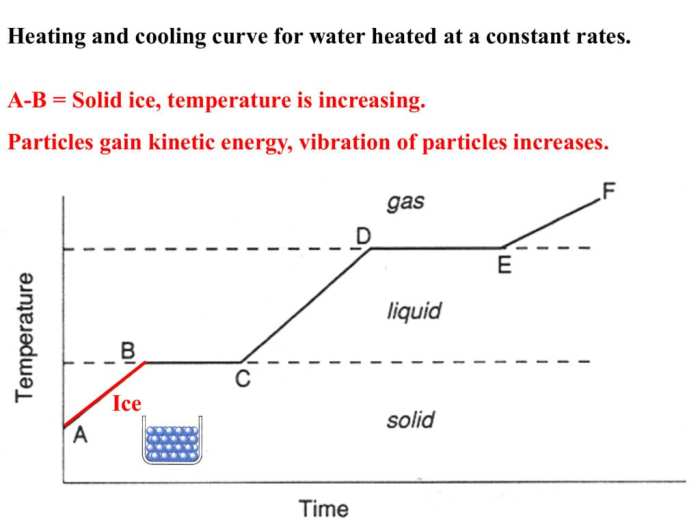
A heating curve is a graphical representation of the temperature change of a substance as it is heated or cooled. It provides valuable insights into the physical and chemical changes that occur during the heating or cooling process.
A heating curve typically consists of several distinct stages, each representing a specific phase transition or change in the substance’s properties.
Stages of a Heating Curve
- Initial Heating:The substance absorbs heat, causing its temperature to rise linearly.
- Melting:The substance undergoes a phase transition from solid to liquid, absorbing heat at a constant temperature (the melting point).
- Boiling:The substance undergoes a phase transition from liquid to gas, absorbing heat at a constant temperature (the boiling point).
- Cooling:The substance releases heat, causing its temperature to decrease linearly.
- Freezing:The substance undergoes a phase transition from liquid to solid, releasing heat at a constant temperature (the freezing point).
- Sublimation:The substance undergoes a phase transition from solid directly to gas, absorbing heat at a constant temperature (the sublimation point).
- Condensation:The substance undergoes a phase transition from gas directly to liquid, releasing heat at a constant temperature (the condensation point).
Worksheet 2 Analysis
Worksheet 2 provides data from a heating curve experiment. The key concepts and calculations involved in analyzing this data include:
Heat Capacity Calculations
The heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to raise its temperature by 1 degree Celsius or Kelvin. It can be calculated using the following formula:
C = Q / (m
ΔT)
where:
- C is the heat capacity in J/g°C or J/gK
- Q is the heat absorbed or released in J
- m is the mass of the substance in g
- ΔT is the change in temperature in °C or K
Enthalpy Changes, Heating curve worksheet 2 answer key
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic property that represents the total thermal energy of a system. The enthalpy change associated with a phase transition is the amount of heat absorbed or released during the transition. It can be calculated using the following formula:
ΔH = Q
where:
- ΔH is the enthalpy change in J
- Q is the heat absorbed or released in J
Applications of Heating Curves
Heating curves have numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Material Characterization:Heating curves can be used to identify and characterize materials based on their thermal properties.
- Phase Transition Studies:Heating curves provide insights into the phase transitions that occur in a substance and the temperatures at which they occur.
- Chemical Analysis:Heating curves can be used to determine the purity of a substance and to identify chemical reactions that occur during heating.
- Thermal Analysis:Heating curves can be used to study the thermal stability and decomposition behavior of materials.
Helpful Answers: Heating Curve Worksheet 2 Answer Key
What is the significance of a heating curve?
A heating curve provides a graphical representation of the temperature change of a substance as it is heated at a constant rate. It reveals the stages of phase transitions, such as melting and boiling, and provides insights into the energetic changes associated with these transitions.
How do I calculate the heat capacity of a substance using a heating curve?
The heat capacity can be calculated by determining the slope of the linear portion of the heating curve. The slope represents the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the substance by one degree Celsius.
What is the enthalpy change associated with melting?
The enthalpy change associated with melting, also known as the enthalpy of fusion, is the amount of heat required to convert a solid into a liquid at its melting point.