Article 250 grounding and bonding answers – As Article 250 takes center stage, we delve into the crucial world of grounding and bonding, unraveling its complexities and illuminating its significance in ensuring electrical safety. This comprehensive guide, meticulously crafted with authoritative insights, promises an immersive journey into the heart of this vital electrical concept.
Grounding, a cornerstone of electrical safety, provides a safe path for fault currents to dissipate into the earth, preventing dangerous voltage buildup on equipment and surfaces. Bonding, on the other hand, ensures that all conductive surfaces within an electrical system are at the same electrical potential, minimizing the risk of electrical shock.
Electrical Grounding Systems: Article 250 Grounding And Bonding Answers
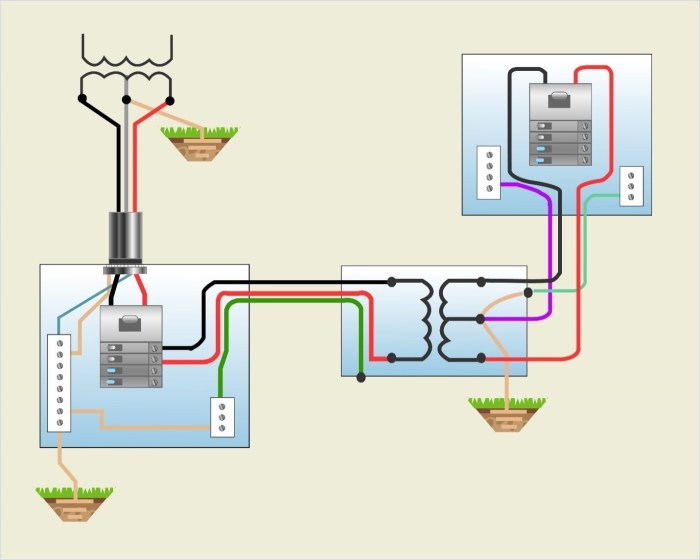
Electrical grounding systems are essential for the safe operation of electrical installations. They provide a path for electrical current to flow to the earth, protecting equipment and personnel from electrical shock and other hazards.
There are three main types of grounding systems used in electrical installations:
- Solidly grounded systems
- Resistance grounded systems
- Ungrounded systems
The type of grounding system used in a particular installation depends on the voltage level, the size of the installation, and the local electrical code requirements.
Grounding Electrodes
Grounding electrodes are used to connect the electrical system to the earth. There are several different types of grounding electrodes, including:
- Ground rods
- Ground plates
- Concrete-encased electrodes
- Water pipes
The type of grounding electrode used in a particular installation depends on the soil conditions, the size of the installation, and the local electrical code requirements.
Bonding and Equipotential Planes
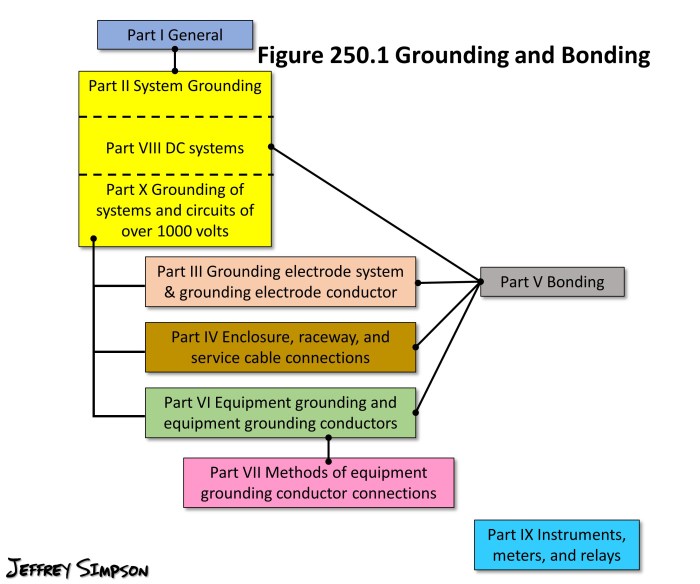
Bonding is the process of connecting two or more electrical conductors together to ensure that they are at the same electrical potential. Bonding is used to prevent electrical shock hazards and to ensure the proper operation of electrical equipment.
There are several different methods of bonding used in electrical installations, including:
- Mechanical bonding
- Electrical bonding
- Chemical bonding
The type of bonding method used in a particular installation depends on the type of materials being bonded and the local electrical code requirements.
Equipotential Planes
Equipotential planes are areas where the electrical potential is the same at all points. Equipotential planes are created by bonding all of the metal objects in an area together. Equipotential planes help to prevent electrical shock hazards by ensuring that there is no difference in electrical potential between any two points.
Ground Fault Protection Devices
Ground fault protection devices (GFCIs) are devices that protect against electrical shock hazards by detecting ground faults and interrupting the flow of electrical current.
There are two main types of GFCIs:
- Circuit breakers
- Receptacles
GFCIs are required in all areas where there is a risk of electrical shock, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas.
Importance of GFCIs
GFCIs are an important safety device that can help to prevent electrical shock hazards. GFCIs are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, and they can save lives.
Testing and Inspection

Grounding and bonding systems should be tested and inspected regularly to ensure that they are functioning properly.
There are several different methods of testing and inspecting grounding and bonding systems, including:
- Visual inspection
- Ground resistance testing
- Bonding resistance testing
The type of test method used in a particular installation depends on the type of grounding and bonding system and the local electrical code requirements.
Importance of Testing and Inspection, Article 250 grounding and bonding answers
Regular testing and inspection of grounding and bonding systems is important to ensure that these systems are functioning properly and that they are providing the necessary protection against electrical shock hazards.
Code Compliance
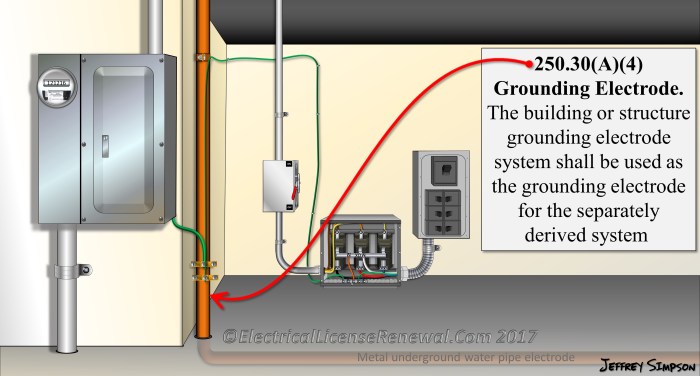
Article 250 of the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides the requirements for grounding and bonding electrical systems.
It is important to adhere to the requirements of Article 250 to ensure that electrical systems are safe and that they are providing the necessary protection against electrical shock hazards.
Common Code Violations
Some of the most common code violations related to grounding and bonding include:
- Improperly installed grounding electrodes
- Inadequate bonding of electrical equipment
- Lack of GFCI protection in areas where it is required
These code violations can create electrical shock hazards and can lead to serious injuries or even death.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the primary purpose of grounding?
Grounding provides a low-resistance path for fault currents to flow into the earth, preventing dangerous voltage buildup on equipment and surfaces.
What is the difference between grounding and bonding?
Grounding connects electrical equipment to the earth, while bonding connects conductive surfaces within an electrical system to each other, ensuring they are at the same electrical potential.
What are the different types of grounding systems?
Common grounding systems include solid grounding, resistance grounding, and isolated grounding.
Why is regular testing and inspection of grounding and bonding systems important?
Regular testing and inspection ensure that grounding and bonding systems remain effective, providing continuous protection against electrical hazards.