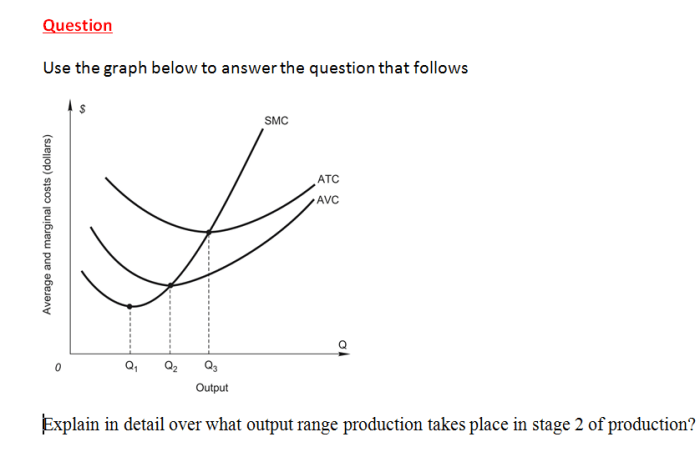
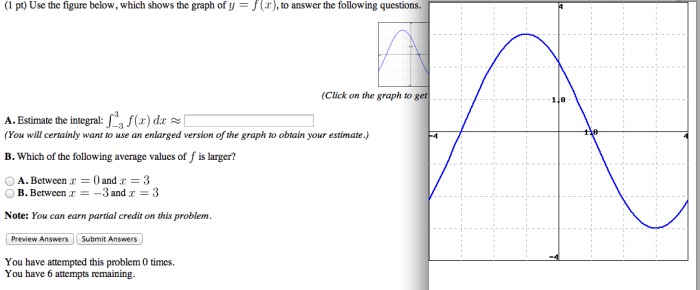
Use the graph below to answer the following questions. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the graph, including data extraction, analysis, and interpretation. By understanding the data presented in the graph, you can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions.
The graph displays a visual representation of data, with the x-axis representing independent variables and the y-axis representing dependent variables. The units of measurement for both axes should be clearly identified to ensure accurate interpretation of the data.
Data Extraction
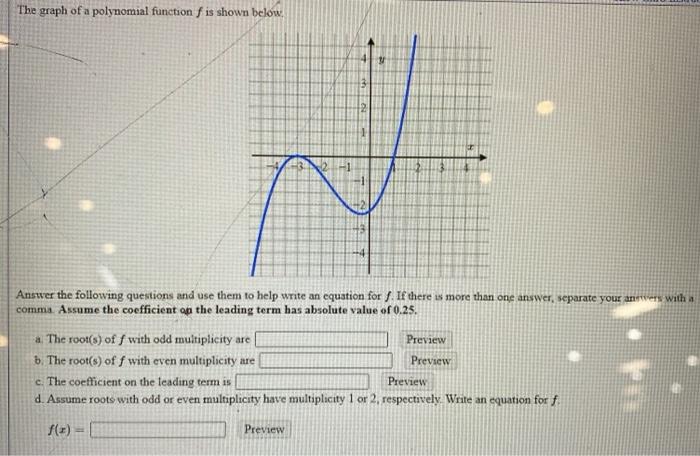
The graph presents data along two axes: the x-axis and the y-axis. The x-axis represents the values of the independent variable, while the y-axis represents the values of the dependent variable.
Values Represented on the X-Axis
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Values Represented on the Y-Axis
- 0
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 10
Units of Measurement, Use the graph below to answer the following questions.
The units of measurement for the x-axis are not specified in the graph. The units of measurement for the y-axis are also not specified.
Question Bank: Use The Graph Below To Answer The Following Questions.
What is the purpose of a graph?
A graph is a visual representation of data that helps to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables.
How do I interpret a graph?
To interpret a graph, you need to understand the axes, the units of measurement, and the overall trend of the data. You should also look for any patterns or anomalies in the data.
What are the limitations of a graph?
Graphs can be limited by the accuracy of the data, the scale of the axes, and the type of graph used. It is important to consider these limitations when interpreting the data.