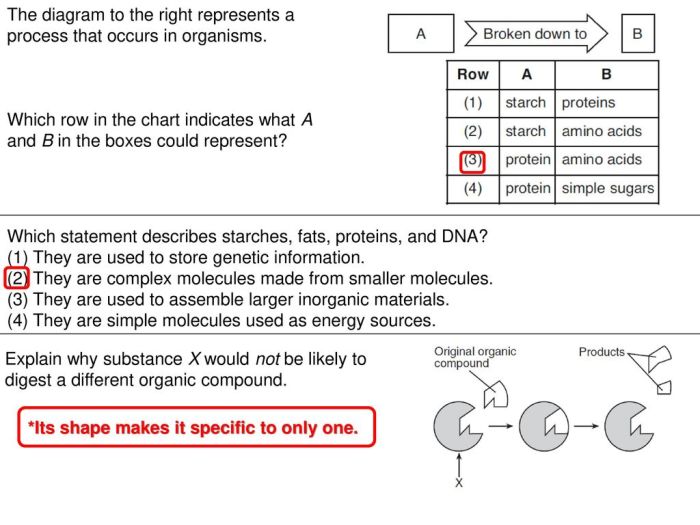
Which statement describes starches fats proteins and dna – This exploration of which statement describes starches, fats, proteins, and DNA embarks on a journey of discovery, unraveling the fundamental characteristics and multifaceted roles of these essential biomolecules. Each molecule holds a unique place in the intricate tapestry of life, contributing to the structure, function, and energy production within biological systems.
Delving into their chemical composition and structure, we uncover the intricate arrangements of atoms and bonds that define their properties and functions. The biological functions of these molecules are equally captivating, as they orchestrate a symphony of cellular processes, from energy metabolism to genetic inheritance.
1. Introduction
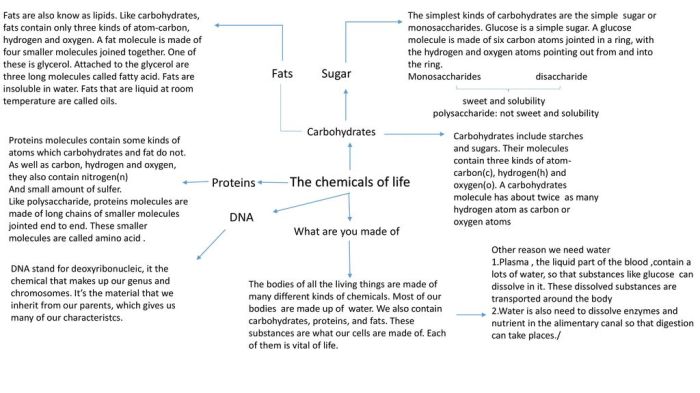
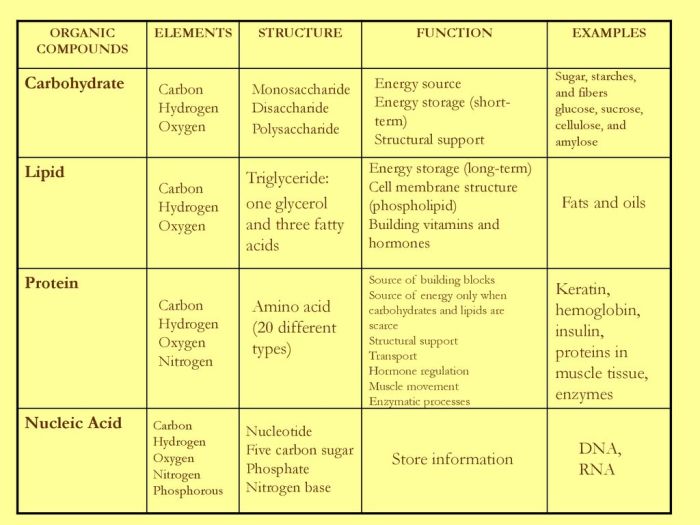
Biomolecules, the fundamental building blocks of life, include starches, fats, proteins, and DNA. Each molecule plays a distinct role in biological systems, contributing to structure, function, and energy production.
2. Chemical Composition and Structure
Starches
Starches, complex carbohydrates, are composed of glucose units linked together in long chains. Their structure, either amylose (unbranched) or amylopectin (branched), influences their solubility and digestibility.
Fats, Which statement describes starches fats proteins and dna
Fats, or lipids, are composed of fatty acids and glycerol. Saturated fats have no double bonds, while unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds, affecting their physical properties and biological functions.
Proteins
Proteins are composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Their structure, including primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, determines their function and stability.
DNA
DNA, the genetic material, is composed of nucleotides (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) linked in a double helix structure. Its sequence determines the genetic code for all living organisms.
3. Biological Functions
Starches
Starches provide energy for cellular processes, particularly in plants. They are stored in organelles called amyloplasts.
Fats, Which statement describes starches fats proteins and dna
Fats provide energy, insulation, and protection. They also serve as a source of essential fatty acids and are involved in hormone production.
Proteins
Proteins perform diverse functions, including structural support, enzyme catalysis, hormone regulation, and immune response.
DNA
DNA stores and transmits genetic information, guiding the development and function of organisms.
4. Metabolism and Energy Production
Starches
Starches are broken down into glucose, which enters glycolysis to produce energy (ATP).
Fats, Which statement describes starches fats proteins and dna
Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation to produce energy.
Proteins
Proteins can be broken down into amino acids, which can be used for energy or to synthesize new proteins.
DNA
DNA does not directly provide energy, but it is essential for cellular processes that require energy.
5. Nutritional Importance
Starches
Starches are an important source of energy for humans and animals. Dietary intake of starches is essential for maintaining blood glucose levels.
Fats, Which statement describes starches fats proteins and dna
Fats are essential for human health, providing energy, absorbing vitamins, and protecting organs.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for growth, tissue repair, and hormone production. Dietary intake of protein is crucial for maintaining nitrogen balance.
DNA
DNA is not typically consumed in the diet, but it plays a crucial role in genetic inheritance and health.
6. Industrial Applications
Starches
Starches are used in food production (e.g., thickening agents), papermaking, and adhesives.
Fats, Which statement describes starches fats proteins and dna
Fats are used in cooking, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. They are also used as biofuels.
Proteins
Proteins are used in food production (e.g., enzymes), pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology.
DNA
DNA is used in genetic engineering, medical diagnostics, and forensic science.
Question & Answer Hub: Which Statement Describes Starches Fats Proteins And Dna
What are the key differences between starches, fats, proteins, and DNA?
Starches are complex carbohydrates that provide energy, fats are lipids that store energy and provide insulation, proteins are amino acid chains that perform diverse functions, and DNA is the genetic material that carries hereditary information.
How do these molecules contribute to biological functions?
Starches provide energy for cellular processes, fats insulate and protect organs, proteins facilitate chemical reactions and transport substances, and DNA stores and transmits genetic information.