Punnett square worksheet dihybrid cross – The Punnett square worksheet for dihybrid cross is an indispensable tool in genetics, providing a structured approach to analyze the inheritance patterns of two different traits. By exploring the intricacies of this worksheet, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of dihybrid crosses, unlocking the secrets of genetic inheritance.
This worksheet guides us through the fundamental concepts of dihybrid crosses, empowering us to calculate genotypic and phenotypic ratios with precision. It serves as a roadmap for predicting the probability of offspring genotypes and phenotypes, laying the groundwork for understanding more complex genetic crosses.
Punnett Square: Overview: Punnett Square Worksheet Dihybrid Cross
A Punnett square is a diagram used in genetics to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a particular mating between two individuals. It is named after Reginald Punnett, a British geneticist who first developed the square in 1905. Punnett squares are particularly useful for analyzing dihybrid crosses, which involve the inheritance of two different traits.
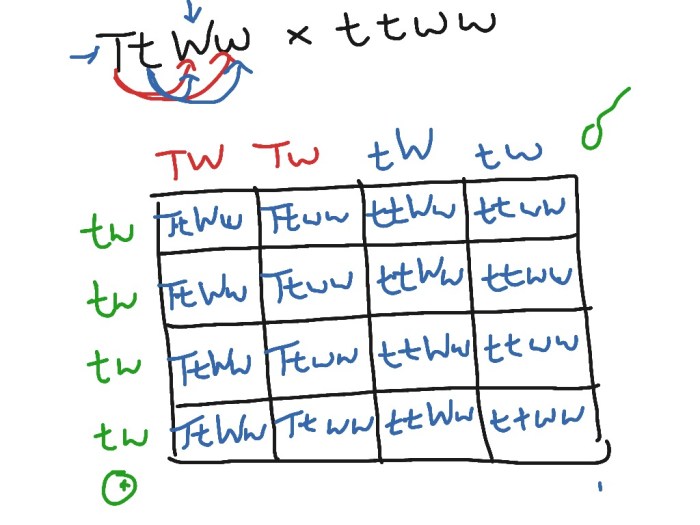
Dihybrid crosses are performed by mating two individuals who are heterozygous for both traits. This means that each parent has two different alleles for each trait. The Punnett square is used to determine the probability of each possible genotype and phenotype in the offspring of the cross.
Components of a Punnett Square
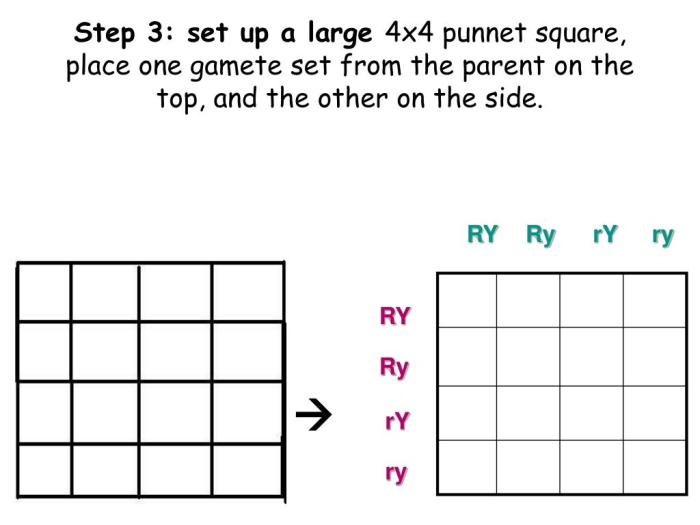
A Punnett square is a grid with rows and columns. The rows represent the possible genotypes of one parent, and the columns represent the possible genotypes of the other parent. The squares within the grid represent the possible genotypes of the offspring.
The genotypes of the parents are written along the top and side of the Punnett square. The alleles for each trait are separated by a slash (/). For example, if a parent is heterozygous for the gene for eye color, their genotype would be written as Bb.
This means that they have one allele for brown eyes (B) and one allele for blue eyes (b).
Calculating Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios
The Punnett square can be used to calculate the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of a dihybrid cross. The genotypic ratio is the ratio of the different genotypes in the offspring. The phenotypic ratio is the ratio of the different phenotypes in the offspring.
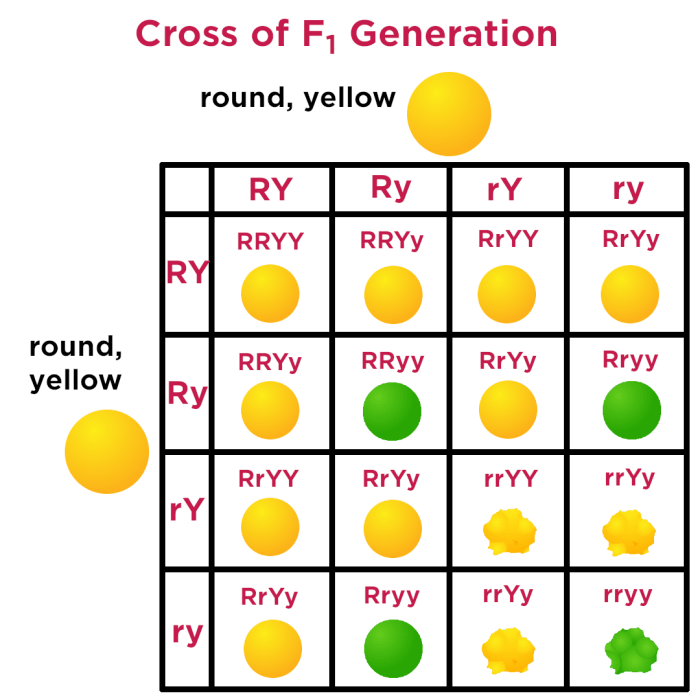
To calculate the genotypic ratio, simply count the number of squares that represent each genotype. For example, if a Punnett square has 9 squares, and 3 of those squares represent the genotype BB, then the genotypic ratio for BB is 3:9.
To calculate the phenotypic ratio, first determine the phenotype of each genotype. For example, if the genotype BB results in the phenotype of brown eyes, and the genotype Bb results in the phenotype of hazel eyes, then the phenotypic ratio for brown eyes to hazel eyes is 3:1.
Example of a Punnett Square Worksheet
A Punnett square worksheet can be used to practice calculating the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of a dihybrid cross. A typical worksheet will include the following information:
- The genotypes of the parents
- A Punnett square
- Instructions on how to complete the worksheet
To complete a Punnett square worksheet, simply follow the instructions provided. Be sure to pay attention to the genotypes of the parents and the alleles that are being inherited.
Advanced Applications of Punnett Squares, Punnett square worksheet dihybrid cross
Punnett squares can be used to analyze more complex genetic crosses, such as those involving multiple alleles or incomplete dominance. They can also be used to predict the inheritance of specific traits.
For example, Punnett squares can be used to predict the inheritance of the ABO blood group. The ABO blood group is determined by three alleles: A, B, and O. The A and B alleles are dominant over the O allele.
This means that individuals with the genotype AA or AO will have type A blood, individuals with the genotype BB or BO will have type B blood, and individuals with the genotype OO will have type O blood.
Punnett squares can also be used to analyze the inheritance of traits that are influenced by multiple genes. For example, height is a trait that is influenced by multiple genes. This means that the height of an individual is not determined by a single gene, but rather by the interaction of multiple genes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a Punnett square worksheet for dihybrid cross?
It provides a structured approach to analyze the inheritance patterns of two different traits in a dihybrid cross.
How do I calculate genotypic and phenotypic ratios using a Punnett square?
Follow the step-by-step guide provided in the worksheet to determine the probability of each genotype and phenotype.
What are the limitations of using a Punnett square?
It assumes complete dominance and does not account for genetic interactions such as epistasis or linkage.